Code
knitr::include_graphics("figures/plan.png")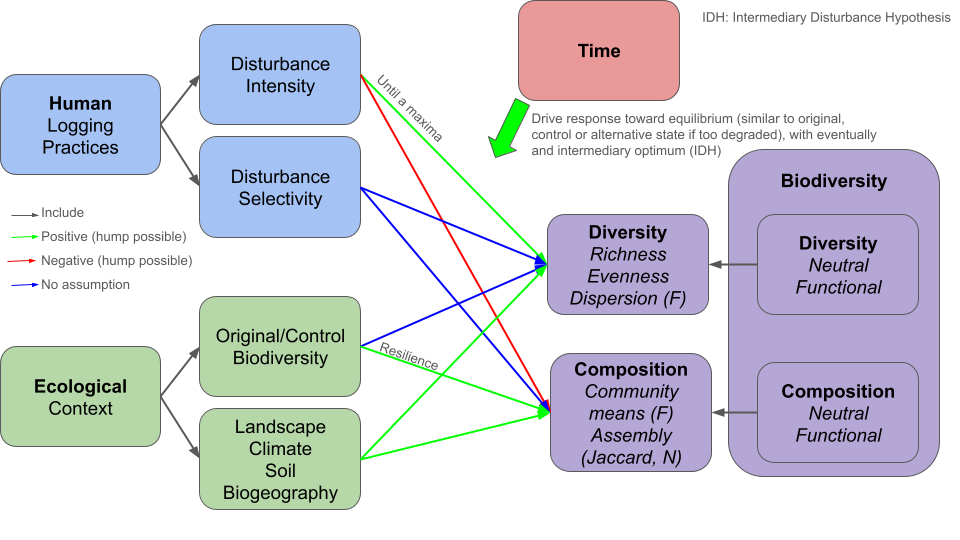
Tree diversity declines initially in response to logging, but then increases through time to a maximum value, after which it then declines in late succession. Tree diversity also shows a non-linear response to increased intensity of logging (proportion of biomass or basal area damaged and/or removed)): lightly logged forests show a transient increase in tree diversity, but more intensively logged forests show a strong negative effect on diversity, which recovers through time to a maximum. Therefore a three-dimensional plot of diversity (z axis) against time and logging intensity/damage shows a peak in the centre of the 3D space. In very heavily logged forests, the recovery of tree diversity takes longer and the maximum of diversity at the mid-point succession may not be observed, indicative of a dampening of the response. Logging intensity moderates/dampens the change in tree diversity through time.
knitr::include_graphics("figures/plan.png")